Your 2024 Guide to Polar Patterns
Photo by Marius Masalar on Unsplash
If you are a beginner music lover and trying to learn about various types of microphone polar patterns, this article is for you. You will learn about different points such as types of microphone polar patterns and their applications in a recording.
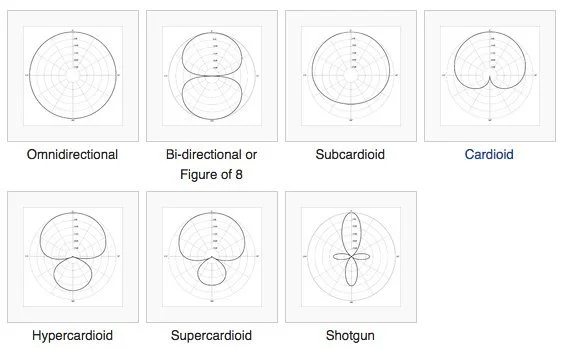
When choosing a microphone, it is important to understand how the different polar patterns work; to choose the right kind. The main goal of any audio/video engineer is to achieve an optimum sound as an end product. Here are four basic polar patterns: omnidirectional, cardioid, figure 8, and bi-directional which we will be explaining and how they can be used to record sound.
What is a polar pattern?
A microphone’s polar pattern is a measurement of its directional characteristics — i.e., where it picks up sound from and where it doesn’t. The most common types of microphones have either omnidirectional (no directionality), cardioid (unidirectional), or figure-8 (bidirectional). A directional mic will pick up sounds from one direction better than another direction, while an omnidirectional one will pick up sounds from all directions equally well.
Photo by William Anders from Quora
Omni-directional (no directionality)
Omnidirectional Mics with this pattern pick up sound equally from all directions, so they’re good for recording an entire ensemble or band without having to worry about pointing it at each performer individually. The downside is that they tend to have more background noise and less gain before feedback than other patterns because they capture more ambient sound than directional ones do.
Cardioid (unidirectional)
The cardioid polar pattern is the most common polar pattern used in recording microphones because it is the most effective at reducing unwanted sounds. It is a unidirectional (uni) polar pattern meaning that it is only sensitive to sounds that are coming from a single direction (cardioid). Some of the uses include: Recording a single vocalist in a live performance.
The pattern is shaped like a heart, hence the name. The microphone is most sensitive along the axis on which the speaker or sound source is located and is least sensitive at the sides and rear. The pickup pattern is illustrated with a polar plot.
Figure 8 (bidirectional)
Figure 8 is a unique, bidirectional polar pattern. It is used in many recording situations because it can pick up the voice directly in front of the microphone and at the same time it can pick up sounds from the rear — which is very useful if you want to record a room or a group of people. This figure-8 microphone is what gives it its special characteristics.
Conclusion
By now, you should have a basic understanding of the different polar patterns used in microphones and how they affect your recording. If you are going to be recording an instrument or voice, then you will want to choose a microphone with the best polar pattern for that application. We hope that this blog post helped learn more about polar patterns and how they can affect your recording. Good luck with your recording work and for more short video tips and tricks on mixing music and other audio-related topics, follow us on Instagram @anadigisoundlab.
17 February 2023